The geologic time scale is a system of chronological dating based on the rock record. It classifies geological layers to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. Over hundreds to thousands of millions of years, continents, oceans and mountain ranges have moved both vertically and horizontally. Areas that were once deep oceans hundreds of millions of years ago are now mountainous or desert regions.
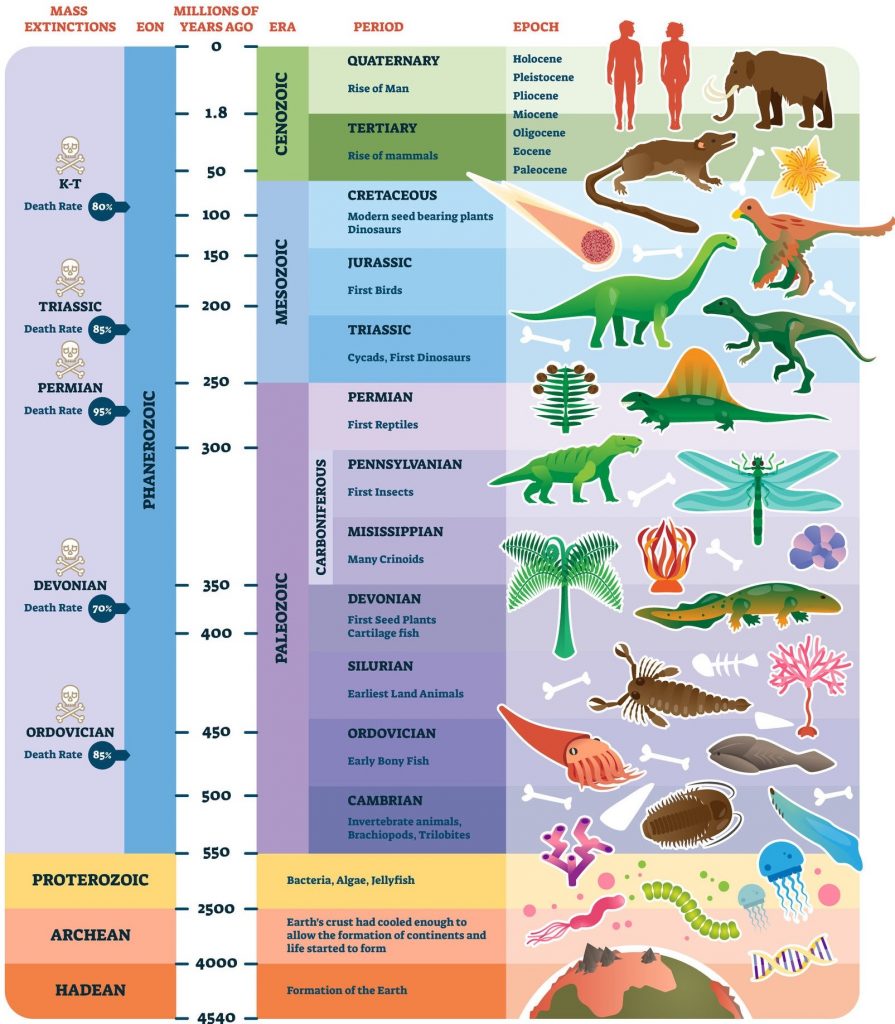
Other subdivisions reflect the evolution of life; the Archean and Proterozoic are both eons, the Palaeozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic are eras of the Phanerozoic eon. The three million year Quaternary period, the time of recognizable humans, is too small to be visible at this scale.
Discover the history of Geologic time
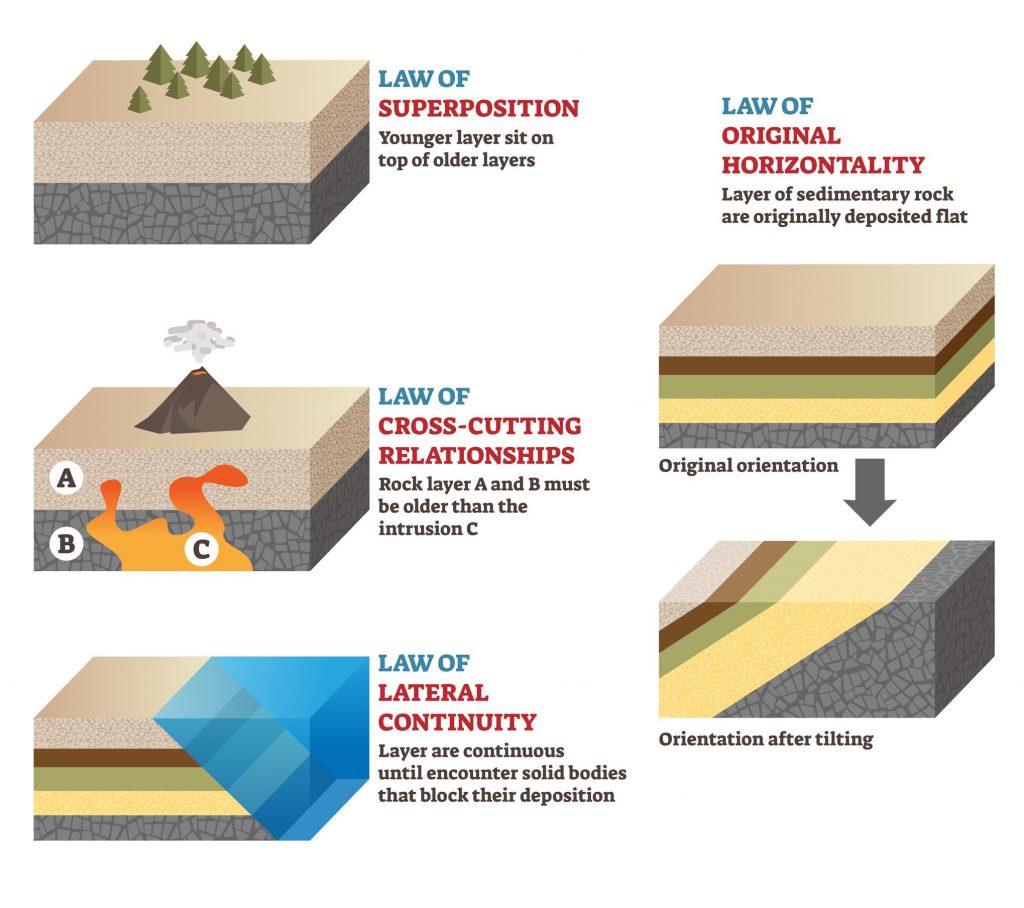
Stenos Law of Stratigraphy
Nicolaus Steno was a 17th-century Danish geologist. His laws of stratigraphy describe the patterns in which rock layers are deposited.
Index fossils
Index fossils are fossils used to define and identify geologic periods. Good examples have a defined time period, wide geographic distribution, abundant and fossilize well.
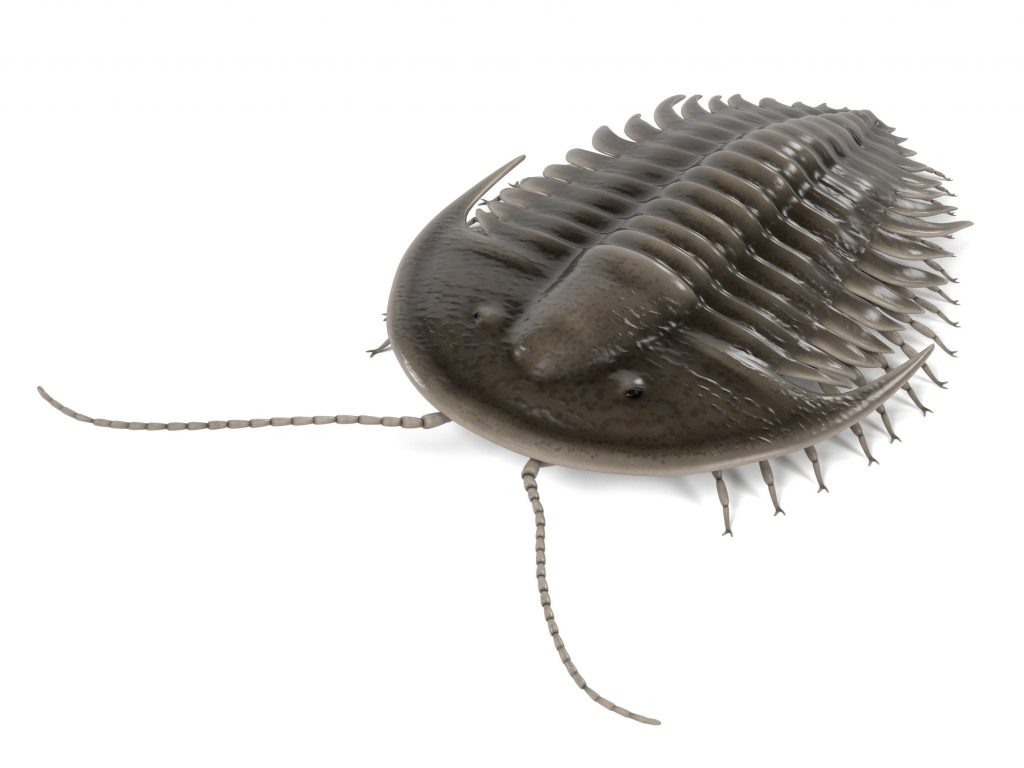
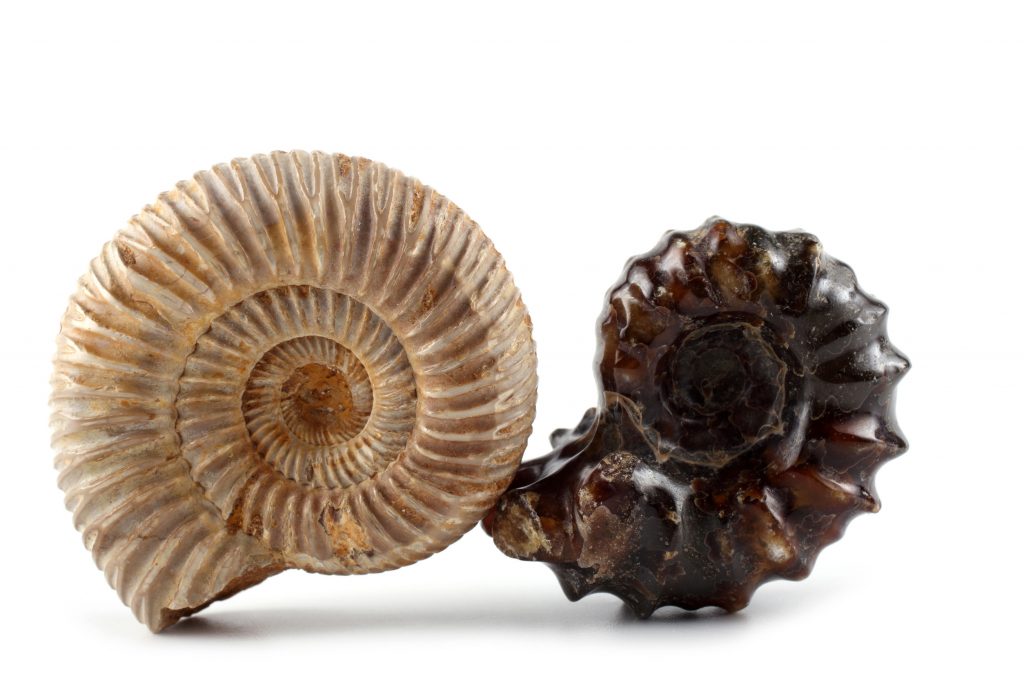


Linked to the relative time scale are examples of index fossils, the forms of life which existed during limited periods of geologic time and thus are used as guides to the age of the rocks in which they are preserved.
Find out more about different time periods
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period is an interval of geological time ranging 635 to 541 million years ago. During this time there was immense geological and biological change. There was a transition from a life largely dominated by microscopic organisms to a world swarming with animals.
Cambrian
There was a vast change in the variety of life on earth during the Cambrian 541 – 485 million years ago. The Cambrian saw the expansion and diversification of multicellular life. The rapid diversification of life forms in the Cambrian is known as the Cambrian explosion. During this time we see the first representatives of all modern animal groups.
Ordovician
Life flourished in the Ordovician 485 – 444 million years ago with molluscs and arthropods dominating the oceans. This was a period of high diversification called the Ordovician radiation. The early vertebrates evolved during this time.
Devonian
The Devonian Period 419 to 359 million years ago is sometimes called the “Age of Fishes” because of the amazing diversity and abundance of fish species. An ocean covered approximately 85 percent of the Devonian globe and the climate is thought to have been warm.
Triassic
The Triassic Period was the first period of the Mesozoic Era and occurred between 251 million and 199 million years ago. It followed the great mass extinction at the end of the Permian Period and was a time when life outside of the oceans began to diversify.

