Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth. Biodiversity is typically a measure of variation at the genetic, species, and ecosystem level. Terrestrial biodiversity is usually greater near the equator, which is the result of the warm climate and high primary productivity.

Genetic diversity
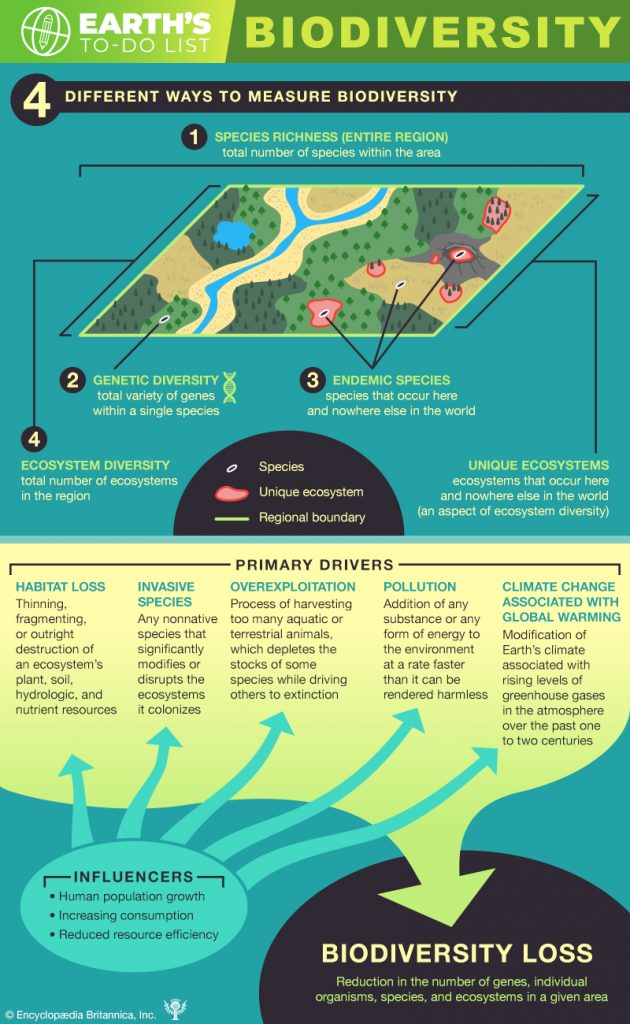
Genetic diversity is the variety of genes within a species. Each species is made up of individuals that have their own particular genetic composition. This means a species may have different populations, each having different genetic compositions. To conserve genetic diversity, different populations of a species must be conserved.
Genes are the basic units of all life on Earth. They are responsible for both the similarities and the differences between organisms.
Not all groups of animals have the same degree of genetic diversity. Kangaroos, for example, come from recent evolutionary lines and are genetically very similar. Carnivorous marsupials, called dasyurids, come from more ancient lines and are genetically far more diverse. Some scientists believe that we should concentrate on saving more genetically diverse groups, such as dasyurids, which include the Tasmanian Devil, the Numbat and quolls.
If we lose one species of dasyurid, we lose a substantial genetic resource. Several species of dasyurids are endangered and at least one, the Tasmanian Tiger, has disappeared forever since Europeans arrived in Australia.
Species diversity
Species diversity is the variety of species within a habitat or a region. Some habitats, such as rainforests and coral reefs, have many species. Others, such as salt flats or a polluted stream, have fewer.
In Australia, more than 80% of plant and animal species are endemic, which means that they only occur naturally in Australia.
Species are grouped together into families according to shared characteristics. In Australia, it is not just the individual species that are endemic – whole families of animals and plants are endemic. Seven families of mammals, four of birds and twelve of flowering plants are endemic to Australia. No other country has as many endemic flowering plant families as Australia.
Invertebrates – animals without backbones – make up about 99% of all animal species, and most of these are insects. Invertebrates include crabs, snails, worms, corals and seastars, as well as insects, such as beetles and flies. Insects fill many vital roles in ecosystems as pollinators, recyclers of nutrients, scavengers and food for others.
While we may mostly notice mammals, they actually make up less than 1% of all animal species.
Ecosystem diversity
Ecosystem diversity is the variety of ecosystems in a given place. An ecosystem is a community of organisms and their physical environment interacting together. An ecosystem can cover a large area, such as a whole forest, or a small area, such as a pond.
An ecosystem is a community of organisms and their physical environment interacting together. An ecosystem may be as large as the Great Barrier Reef or as small as the back of a spider crab’s shell, which provides a home for plants and other animals, such as sponges, algae and worms.
Learn more at the Australian Museum
Australian Environmental Education Biodiversity resources
Attracting birds to your backyard
Attract birds to your backyard by creating a garden that will provide food, shelter and nesting materials and sites. Local flowering plants and fruit trees provide birds with nectar and seeds. To provide birds with some protein rich food, use mulch to encourage worms, insects and grubs to thrive. Plant dense prickly native shrubs for shelter, hang up nesting boxes and install a bird bath.
Create a frogs friendly backyard
Encourage frogs to come to live and breed in your backyard. Create a small shallow pond in an area that is partly shaded. Include thick ground hugging plants around part of the pond to provide areas of warmer and cooler water. Your pond will need some sunlight to encourage algae and other plants that provide food for tadpoles. Make sure the banks slope gently so that the frogs can get out. Add some rocks and logs to provide shelter for adult frogs.
Minibeasts in your backyard
Not all bugs are pests. Good bugs pollinate plants, break down dead flora and fauna, aerate the soil and provide for other wildlife. They can even help keep harmful pests away. Create an inviting environment for good bugs by planting plenty of native plants, wildflowers and herbs and use chemical-free pest control when the pests do creep in.
Life Cycles
A life cycle refers to the stages or changes that an animal goes through while it’s alive. There are different types of life cycles depending on the species. Vertebrates typically have three stages to their life cycle: egg, juvenile and adult. Amphibians differ to other vertebrates and undergo metamorphosis.